
The ssh-agent is a session service that stores keys temporarily for the user.
MAC RESTART SSH AGENT HOW TO
Source: Super User - How to use Mac OS X Keychain with SSH keys?

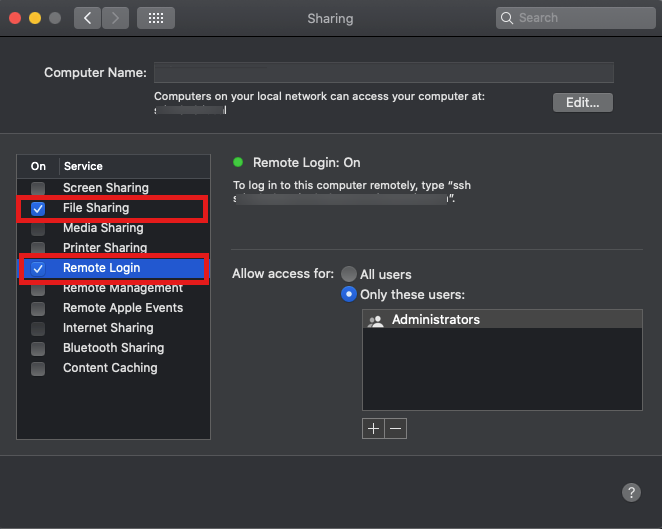
You should be able to see the keys in the Keychain Access app, as well as from the command line via: ssh-add -l Whenever you reboot your Mac, all the SSH keys in your keychain will be automatically loaded. Your keys should then persist from boot to boot. So from the sound of it you could import your SSH keys into Keychain using this command: $ ssh-add -K
Could someone please explain how this feature is supposed to work. I understand that since Mac OS X Leopard the Keychain has supported storing SSH keys.
I do not use OSX but did find this Q&A on SuperUser titled: How to use Mac OS X Keychain with SSH keys?. You can activate this feature by adding UseKeychain yes to your ~/.ssh/config. Starting with macOS Sierra 10.12.2, Apple has added a UseKeychain config option for SSH configs. ssh-add -l displays the identities currently held by the agent. Several identities can be stored in the agent the agent can automatically useĪny of these identities. If neither of these is the case then the authentication will fail. Passphrase on the terminal if it has one or from a small X11 program if running under X11. If the identity has a passphrase, ssh-add(1) asks for the When executed without arguments, ssh-add(1) adds theįiles ~/.ssh/id_rsa, ~/.ssh/id_dsa, ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa and ~/.ssh/identity. The agent initially does not have any private keys. Use of environment variables the agent can be located and automatically used for authentication when logging in to other machines using
MAC RESTART SSH AGENT WINDOWS
The beginning of an X-session or a login session, and all other windows or programs are started as clients to the ssh-agent program. Ssh-agent is a program to hold private keys used for public key authentication (RSA, DSA, ECDSA). If you kill it or restart your computer they're lost until you re-add them again. They last only so long as the agent is running. To access the fail2ban configuration file, enter the following command: sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/nfĮdit the file by uncommenting the line that contains "ignoreip =" add the IP or IP range you want to white-list.The addition of keys to the agent is transient. Otherwise, the service is going to block all future attempts continuously. If you find that a firewall is indeed preventing your SSH connection, you can white-list your IP with fail2ban. The output in your terminal window is going to list all authentication attempts. In our example, we used the following command to check if the iptables tool is rejecting your attempted connections: sudo iptables -L -line-number It monitors logs, like the ny and hosts.allow files we edited previously. Fail2ban is a service designed to protect you from brute force attacks, and it can misinterpret your authentication attempts as an attack.įail2ban monitors and dynamically alters firewall rules to ban IP addresses that exhibit suspicious behavior. If you’ve tried to connect on multiple occasions, your IP might be blocked by an intrusion prevention software. Keep in mind that such a limiting security setting can affect administering capabilities on your remote servers. By adding the following line, only the following IP would be allowed to establish an SSH connection with your remote server: sshd : 10.10.0.5, LOCAL Subsequently, you can add a single IP address, an IP range, or a hostname to the etc/hosts.allow file. For example, a strict security policy within the etc/ny file, would deny access to all hosts: sshd : ALL


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
